Automate Your Deployment Pipeline for Scalable Releases
Modern engineering teams move fast. Products evolve daily and customers expect frequent updates.
Manual deployment processes introduce delays and inconsistencies — automated CI/CD pipelines
deliver a standardized, repeatable release workflow that improves velocity and stability.
1. Understanding CI/CD Principles
CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery
(or Continuous Deployment). These practices help teams bring code changes into production
quickly and safely.
Continuous Integration encourages frequent merges so automated builds and tests run immediately.
Continuous Delivery ensures every validated build is ready for release. Continuous Deployment
automates the final rollout to production. The goal: shorter delivery cycles, reduced manual
intervention, and consistent quality across environments.
2. Why Automated Deployment Pipelines Matter
Manual deployments consume engineering time, slow releases, and create opportunities for errors.
Automated pipelines remove repetitive tasks and ensure Development, Staging, and Production follow
the same predictable workflows.
Key benefits include:
- Faster feedback loops
- Higher release frequency
- Fewer hotfixes
- Stronger developer confidence
- Better alignment between product and engineering
3. Steps to Set Up an Automated Pipeline
A robust CI/CD pipeline moves code from commit to production in a controlled, visible way. Typical
elements include:
Integrated Version Control
The pipeline should react immediately to pushes. Tight integration between version control and CI/CD
validates commits early and ensures traceability of changes across environments.
Automated Build and Packaging
A consistent build eliminates differences caused by local developer setups. Packaging artifacts
consistently improves predictability and reduces last-minute surprises.
Layered Testing
Run tests in layers: unit tests for logic, integration tests for module interactions, and quality gates
to prevent unstable code progressing. Properly structured testing acts as a guardrail rather than a bottleneck.
Environment Deployments
Automate deployments for each environment using repeatable scripts or manifests. Consistent provisioning
prevents environment drift so Development, Staging, and Production behave similarly.
Approvals and Notifications
Keep human intervention to steps that add value (final reviews, sensitive releases). Automated notifications
keep stakeholders aware of progress, failures, and approvals without slowing teams down.
Rollback Paths
Plan for failure with automated or near-instant rollback mechanisms. Rollbacks reduce the impact of
problematic releases and increase team confidence.
4. Popular CI/CD Tools: Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI
Teams rely on several trusted tools to automate pipelines. Choose based on your ecosystem, scalability needs,
and preferred automation style.
- Jenkins — an industry-standard automation server with extensive plugin support and deep customization.
- GitHub Actions — native CI/CD for GitHub repositories; easy adoption and reusable workflows.
- GitLab CI — a full DevOps platform that combines code management, pipelines, monitoring, and security.
Other notable options: CircleCI, Azure DevOps, and cloud-native pipeline services depending on your platform.
5. Common Pitfalls and Practical Fixes
Common issues teams face and how to address them:
Inconsistent Environments
Problem: Environments configured independently cause unpredictable behavior. Fix: Use standardized templates,
shared configuration files, and automated provisioning to eliminate drift.
Pipelines That Try to Do Everything
Problem: Overloaded pipelines slow builds and increase maintenance. Fix: Start with essentials, mature gradually,
and expand based on measured needs.
Unstable Tests
Problem: Flaky tests break trust in automation. Fix: Stabilize tests, remove unreliable scripts, and group tests
by purpose.
Poor Visibility
Problem: Failures are hard to diagnose. Fix: Add dashboards, centralized logs, and integrated notifications for clear pipeline status.
Missing Rollback Paths
Problem: No rollback forces firefighting during incidents. Fix: Implement rollback scripts, versioned artifacts,
and automated restore steps.
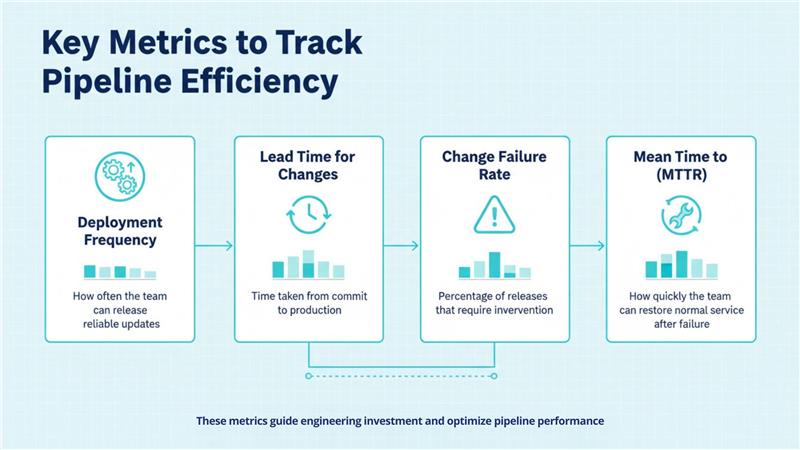
6. Key Metrics to Track Pipeline Efficiency
Track these metrics to ensure automation delivers value:
- Deployment Frequency
- How often your team releases reliable updates.
- Lead Time for Changes
- Time from commit to production.
- Change Failure Rate
- Percentage of releases that cause incidents or need intervention.
- Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR)
- How quickly normal service is restored after a failure.
Use these metrics to prioritize improvements and measure the real impact of CI/CD investments.
7. AcmeMinds Case Study: Modernizing Deployment with Automated CI/CD Pipelines
A technology company approached AcmeMinds with slow, inconsistent, and overly manual deployment cycles.
Environments followed different steps, visibility was low, and coordinating releases consumed valuable time.
AcmeMinds implemented a Jenkins-driven CI/CD pipeline: automated builds on every commit, structured deployments
across Development, Staging, and Production, quality gates to ensure stability, improved notifications, and robust
rollback support.
Results within weeks:
- Deployment cycles ran 80% faster
- Release frequency tripled
- Manual steps vanished
- Deployment errors dropped by more than 90%
- Unified visibility through a single pipeline
Automation enabled predictable, repeatable, and scalable software delivery for the organization.
Final Takeaway
Automated CI/CD pipelines provide the speed and stability teams need to ship software consistently. They reduce human
error, strengthen collaboration, and enable rapid iteration without sacrificing quality. Whether you adopt Jenkins,
GitHub Actions, or GitLab CI, a well-structured pipeline is the backbone of modern software delivery.
Teams ready to modernize their deployment workflow can look to solutions like AcmeMinds for end-to-end CI/CD enablement.
Automation delivers lasting impact and scales as your product grows.
FAQs
1. What is the main purpose of a CI/CD pipeline in software development?
A CI/CD pipeline automates building, testing, and deploying code to reduce manual effort and human error,
helping teams ship software faster, more frequently, and with greater stability.
2. How does automated deployment improve release quality?
Automated deployment enforces consistent, repeatable steps for every release, reducing bugs and last-minute surprises,
and ensuring smoother rollouts across all environments.
3. Do small teams or startups really need CI/CD?
Yes. CI/CD helps small teams move quickly, catch issues early, and focus on product work instead of manual deployment tasks.
4. What tools are most commonly used to set up CI/CD pipelines?
Common tools include Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, CircleCI, and Azure DevOps. The best choice depends on your
workflow, tech stack, and scalability requirements.
5. How long does it take to implement a CI/CD pipeline for an existing application?
Timelines vary: simple pipelines can be set up in a few days; complex workflows with multiple environments and tests
can take a few weeks.
6. What are the biggest challenges teams face when adopting CI/CD?
Major challenges include integrating legacy apps, aligning development and operations, and creating reliable automated tests.
Treat CI/CD as an ongoing improvement cycle rather than a one-time setup.