Production-Grade Generative AI in Enterprise Software
Generative AI is rapidly becoming a core capability in enterprise software. Organizations are moving beyond experiments to embed large language models into products, applications, and internal platforms. Gartner states that by 2026, over 80 percent of enterprises will have deployed generative AI APIs or applications, compared to less than 5 percent in 2023. As adoption accelerates, the real challenge is no longer access to models but building production-ready systems that are secure, scalable, and reliable. This requires disciplined architecture, strong data engineering foundations, and operational controls designed for enterprise environments.
Why Enterprise Generative AI Pilots Fail in Production
Most enterprise GenAI initiatives begin with controlled pilots. These pilots typically rely on static prompts, limited datasets, and a narrow set of users. While such implementations demonstrate potential, they fail to account for the realities of production environments.
In production, systems must handle unpredictable user behavior, concurrent requests, fluctuating traffic patterns, and evolving enterprise data. Latency expectations become stricter, costs scale exponentially, and failure modes multiply. Without architectural guardrails, small inefficiencies cascade into reliability and governance risks.
Another common failure point is embedding logic directly into prompts. Prompt-centric designs are fragile. They are difficult to version, hard to test, and nearly impossible to audit. Enterprises quickly discover that experimentation success does not translate into operational reliability.
What Defines Production-Grade Generative AI in Enterprise Software
Production-grade Generative AI systems prioritize predictability over novelty. They are designed to operate as dependable enterprise services rather than experimental features.
Key defining attributes include:
- Controlled data access aligned with enterprise security policies
- Repeatable and testable inference behavior
- Full traceability from input to output
- Operational visibility across cost, latency, and quality
Enterprise systems must explain not only what an AI generated, but also why and from which data sources. This requirement fundamentally differentiates enterprise GenAI from consumer applications.
Reference Architecture for Enterprise LLM Applications
A scalable GenAI architecture separates responsibility across clearly defined layers.
User Interaction Layer
Interfaces embedded within enterprise applications capture intent and enforce input validation. This layer prevents malformed or malicious inputs from reaching the model.
Orchestration and Control Layer
This layer manages prompt templates, contextual assembly, routing logic, and guardrails. It ensures consistency and enforces governance policies centrally.
Inference Layer
Models are invoked through managed APIs or internal inference clusters. Version pinning and controlled rollout strategies prevent unexpected behavior changes.
Integration Layer
Enterprise systems such as CRMs, ERPs, data warehouses, and document repositories are accessed through secured connectors.
This modular design allows teams to evolve each layer independently.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation as an Enterprise Standard
Enterprises cannot rely on model knowledge frozen at training time. Business data is dynamic, regulated, and proprietary.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation addresses this by injecting verified enterprise context into every request. Instead of generating responses from probabilistic memory, the model reasons over retrieved documents and structured records.
Enterprise use cases
- Compliance assistants referencing internal policy documents
- Customer support platforms grounded in current product documentation
- Internal knowledge systems spanning contracts, SOPs, and reports
RAG significantly reduces hallucinations and aligns outputs with enterprise truth.
Data Engineering Foundations for Enterprise GenAI
High-quality outputs depend on disciplined data engineering.
Enterprise GenAI platforms require pipelines that ingest structured records, unstructured documents, logs, and events. Data must be cleaned, classified, enriched with metadata, and versioned to ensure consistency.
Embedding strategies must align with data types and retrieval use cases. Chunking decisions directly impact recall and precision. Without proper data lifecycle management, retrieval quality degrades rapidly.
Security, Privacy, and Compliance in Generative AI Systems
Security risks in GenAI systems extend beyond traditional application threats.
Key controls include
- Role-based access to retrieved content
- Prompt sanitization to prevent injection attacks
- Output filtering for sensitive data exposure
- Isolation between tenants and users
Compliance requirements demand full audit trails. Every request, retrieval, and response must be traceable for regulatory review.
GenAI MLOps and Lifecycle Management
Generative AI systems are dynamic, they learn, adapt, and rely on constantly changing data. To ensure reliability in production, enterprises need robust MLOps practices tailored for GenAI.
Key considerations include:
- Versioning: Maintain clear version control for prompts, embeddings, retrieval pipelines, and models. This ensures reproducibility, auditability, and safe experimentation.
- Canary Releases & Feature Gating: Deploy changes to a small subset of users or traffic first, validating performance and quality before full rollout. This mitigates risk and allows safe iteration.
- Rollback Mechanisms: Rapidly revert to previous stable versions if outputs degrade or unexpected behaviors appear, minimizing downtime and business impact.
- Monitoring & Feedback Loops: Track performance, accuracy, grounding, latency, and user interactions continuously. Automated alerts combined with human-in-the-loop oversight help detect drift or anomalies early.
Without disciplined lifecycle management, GenAI platforms can quickly become brittle, unpredictable, and difficult to maintain. A structured MLOps approach ensures systems evolve safely, remain reliable, and continue delivering measurable business value.
Enterprise GenAI Implementation Roadmap
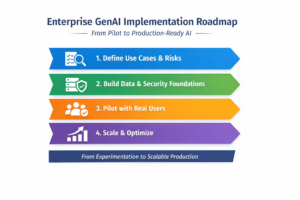
Implementing Generative AI in an enterprise is not just about adopting the latest models, it requires a structured, phased approach to balance innovation with risk, scalability, and performance. Here’s a deeper dive into each phase:
Phase 1: Define Use Cases, Data Constraints, and Risk Tolerance
- Use Case Prioritization: Identify high-impact business processes where GenAI can deliver measurable value, such as automated report generation, customer support, or code completion. Rank use cases based on ROI, complexity, and regulatory requirements.
- Data Assessment: Catalog available internal and external data sources, and evaluate their quality, completeness, and freshness. Identify sensitive datasets that may require anonymization or cannot leave the enterprise boundary.
- Risk Profiling: Define acceptable levels of model errors, hallucinations, or biases for each use case. Establish guardrails for compliance, intellectual property, and security considerations.
- Success Metrics: Decide upfront how success will be measured – response accuracy, time saved, engagement metrics, or cost reduction.
Phase 2: Build Retrieval Pipelines, Security Controls, and Observability Foundations
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Pipelines: Set up pipelines that combine vector databases, semantic search, and knowledge graphs to provide contextually accurate answers.
- Security Controls: Implement encryption for data at rest and in transit, access controls, role-based permissions, and auditing. Consider on-premises or hybrid deployments for sensitive workloads.
- Observability: Integrate logging, monitoring, and alerting for model inference, data drift, and latency. Track usage patterns to identify potential misuse or unexpected outputs.
- Versioning and Experimentation: Maintain model, dataset, and pipeline versioning to reproduce results and roll back in case of errors.
Phase 3: Deploy Limited Pilots with Real Users and Real Data
- Pilot Deployment: Launch controlled experiments with a subset of users or teams. Ensure pilots cover edge cases and stress scenarios.
- Feedback Loop: Collect structured feedback on model outputs, usability, and business impact. Use this data to fine-tune prompts, model parameters, and retrieval sources.
- Performance Monitoring: Measure latency, throughput, and infrastructure costs. Track user satisfaction and model accuracy metrics to identify gaps before scaling.
- Iterative Tuning: Refine models and pipelines in cycles, focusing on reducing hallucinations, improving relevance, and maintaining compliance.
Phase 4: Scale Across Teams and Products with Cost and Performance Optimization
- Horizontal Scaling: Extend GenAI capabilities across multiple teams, departments, and products while maintaining security and compliance standards.
- Cost Optimization: Leverage batch processing, model distillation, or mixed-precision inference to reduce compute costs. Use auto-scaling and spot instances where feasible.
- Performance Engineering: Optimize model serving with caching, prompt engineering, and RAG optimizations to minimize latency and improve throughput.
- Governance and Lifecycle Management: Implement ongoing model audits, retraining schedules, and access controls. Maintain clear documentation of model lineage, data sources, and decision logic for compliance and future audits.
This phased approach allows enterprises to innovate rapidly with Generative AI while maintaining control over risk, compliance, and cost. By starting small, building technical foundations, and scaling systematically, organizations can maximize impact without compromising security or reliability.
Metrics That Matter for Generative AI Success
Measuring the success of enterprise Generative AI is about more than technical performance, it’s about connecting AI outputs to business impact. The right metrics ensure teams can make informed decisions, optimize resources, and scale solutions confidently.
Cost per Request and per User
- Tracks the operational efficiency of your GenAI platform.
- Helps balance model complexity with infrastructure costs.
- Guides decisions on batch processing, caching strategies, and workload-aware model selection to keep ROI positive.
Grounding Accuracy and Relevance
- Measures how well model outputs align with verified enterprise data.
- Critical for reducing hallucinations and ensuring compliance in sensitive applications like contracts, legal advice, or customer support.
- Can be tracked using automated evaluation pipelines, human review, or feedback loops integrated into workflows.
Latency Under Peak Load
- Evaluates system responsiveness in real-world conditions.
- Ensures that AI-powered features integrate seamlessly into enterprise applications without slowing down user workflows.
- Highlights bottlenecks in inference, retrieval, or orchestration layers for targeted optimization.
Adoption and Workflow Completion Rates
- Tracks actual usage and user engagement with AI features.
- Measures whether AI is helping employees or customers achieve tasks more efficiently.
- Low adoption signals potential usability issues, lack of trust, or misalignment with business needs that drive iterative improvements.
Additional Metrics to Consider
- Error Recovery Rate: How often the system gracefully handles unexpected inputs or failures.
- Prompt Efficiency: How many tokens or API calls are needed to get accurate outputs, impacting cost and latency.
- Model Drift Detection: Measures shifts in output quality over time as data or user behavior changes.
- Business Impact Metrics: Reduction in time-to-completion, cost savings, increased revenue, or improved customer satisfaction tied to AI outputs.
By combining these technical and business-focused metrics, enterprises can continuously optimize Generative AI deployments. Metrics not only evaluate current performance but also guide prioritization, resource allocation, and strategic investment decisions ensuring that AI initiatives deliver measurable value.
Conclusion
Generative AI can transform enterprise software but only when built for production. Secure architecture, reliable data pipelines, and phased scaling turn experimentation into impact. AcmeMinds helps enterprises deploy GenAI that’s scalable, compliant, and business-ready. Learn more in our practical guide for product teams on integrating AI features in modern applications.
FAQs
1. What makes Generative AI enterprise-ready?
Generative AI becomes enterprise-ready when it is built on secure architecture, supported by reliable data pipelines, enforced with governance controls, and continuously monitored in production. These foundations ensure scalability, compliance, and dependable performance.
2. Why is Retrieval-Augmented Generation critical?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation grounds AI responses in verified enterprise data sources. This approach reduces hallucinations, improves accuracy, and significantly lowers compliance and regulatory risks in business-critical applications.
3. How do enterprises control GenAI costs?
Enterprises manage GenAI costs through token optimization, intelligent caching, and workload-aware model selection. These techniques help balance performance and accuracy while keeping inference and operational expenses predictable.
4. What teams should own GenAI platforms?
GenAI platforms are typically owned by platform engineering or data engineering teams. Close collaboration with security teams ensures strong access controls, compliance alignment, and safe enterprise-wide adoption.
5. How is GenAI different from traditional ML?
Unlike traditional machine learning, Generative AI requires continuous context management and output governance. Beyond training models, teams must manage prompts, retrieved data, and generated outputs in real time.
6. Can GenAI systems be audited?
Yes, GenAI systems can be audited when designed with comprehensive logging, traceability, and version control. These capabilities enable accountability, compliance reporting, and post-incident analysis.