How AcmeMinds Builds Cloud-Native Apps That Last
As digital platforms scale, traditional application architectures struggle to deliver the speed, resilience, and cost control that today’s enterprise systems demand. This is where cloud-native application development becomes the foundation for long-term performance.
At AcmeMinds, we build enterprise-grade cloud-native applications designed to scale securely from day one. Our approach combines secure cloud app deployment, modern cloud infrastructure management, and proven AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud best practices to deliver platforms that remain reliable, adaptable, and cost-efficient as your business grows.
In this guide, we break down how we architect cloud-native systems that last, from platform selection and CI/CD automation to observability, reliability engineering, and FinOps-driven cost control.
1. Why cloud-native matters for long-term enterprise success
For enterprises adopting or modernizing digital systems, the biggest challenge is not building an application – it’s keeping it scalable, secure, and cost-efficient as usage grows. Cloud-native engineering addresses exactly that problem.
A CNCF survey shows that 82% of organizations plan to use cloud-native platforms as their primary environment for new applications, a strong signal that the industry is shifting toward architectures designed to scale, self-heal, and support long-term growth.
This shift aligns with what we experience at AcmeMinds daily:
Enterprises want modern application development, faster deployment cycles, predictable operations, and cloud infrastructure management that doesn’t become a burden.
Cloud-native principles allow us to build apps that scale and evolve with time.
2. Core principles that create truly scalable applications
We treat cloud-native development as a comprehensive engineering practice. Instead of building features in isolation, we architect systems that behave reliably under real-world load. Our core principles include:
Modular, service-oriented design
Microservices, domain-driven boundaries, independent scaling, and controlled blast radius. This structure is essential for scalable application behavior during spikes.
Infrastructure as Code
Terraform, CloudFormation, and Git-based workflows allow every environment like development, staging, production to be reproducible and governed. This reduces operational drift and improves compliance.
Platform engineering
We build internal developer platforms that standardize CI/CD, container templates, deployment rules, and observability.
Result: faster onboarding, consistent app deployment, reduced cognitive load for engineering teams.
Security built into every layer
Zero-trust policies, least-privilege access (IAM), secrets encryption, automated vulnerability scanning, and compliance monitoring.
Observability from day one
Metrics, logs, and distributed tracing embedded into each service enable real-time debugging, capacity planning, and proactive reliability improvements.
These principles together ensure the application remains adaptable even as infrastructure, users, or business needs evolve.
3. How we choose the right cloud platform: AWS, Azure, or GCP
Each cloud provider has strengths. We help clients select the one that aligns with their priorities of either performance, compliance, data tooling, integration requirements, or cost.
When we choose AWS
- Strong managed databases (Aurora, DynamoDB)
- Enterprise-grade IAM
- Mature Kubernetes (EKS) and serverless stack
- Ideal for healthcare, BFSI, SaaS scale-ups
When we choose Azure
- Deep Microsoft ecosystem integration
- Active Directory alignment
- Strong enterprise governance tools
- Good for large enterprises with existing MS workloads
When we choose GCP
- Advanced analytics & AI services
- Rapid autoscaling
- Strong developer experience
- Suitable for data-heavy and ML-driven apps
This approach ensures your cloud-native foundation is resilient and future-ready.
4. CI/CD, containerization & modern app deployment foundations
An enterprise cloud app must deploy safely, frequently, and predictably. Our pipelines enable:
Standardized containers
Docker images and Kubernetes orchestration (EKS, AKS, GKE) provide consistency across environments and support auto-scaling.
GitOps automation
Declarative deployments, versioned state, rollbacks, and continuous reconciliation for stable, audit-ready deployments.
Safe rollout techniques
- Canary deployments
- Blue-green deployments
- Feature flags
These reduce risk in production releases and improve uptime.
Automated testing
Unit, integration, contract, and smoke tests run fully in CI, improving developer velocity and reducing production defects. This is the backbone of reliable, repeatable app deployment for enterprise workloads.
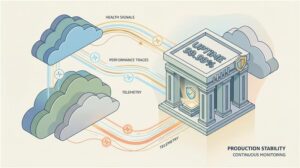
5. Observability, reliability engineering & cloud infrastructure management
Long-term success depends on how the application behaves in production. Our team embeds SRE (Site Reliability Engineering) and observability principles into every system.
Complete visibility
- Metrics (Prometheus)
- Logs (ELK)
- Tracing (OpenTelemetry, Jaeger)
Reliability guarantees (SLOs)
We define SLIs and SLOs that reflect real user impact (latency, availability, throughput).
Automated operations
- Health-based autoscaling
- Self-healing pods
- Automated remediation scripts
- Intelligent alerting to reduce noise
These reduce operational burden and enable predictable cloud infrastructure management as the application scales.
6. Cost governance & FinOps practices
Cloud costs can escalate fast. We integrate FinOps so cost never becomes a blocker.
Key FinOps practices
- Resource rightsizing
- Reserved vs spot instances
- Efficient storage tiering
- Cost tagging for ownership
- Monthly optimization reviews
- Workload scheduling to avoid idle billing
This combination ensures long-term sustainability for enterprise cloud apps without compromising performance or resilience.
7. Case Highlight: Patient Xperience Boost – AWS cloud-native healthcare app
We built Patient Xperience Boost, a healthcare web and mobile application, using AWS-native services. Healthcare workloads require high security, strict uptime, and smooth user experience making cloud-native patterns essential.
What we implemented
- Microservices running on AWS containers
- Secure IAM and data isolation
- CI/CD pipelines for rapid deployment
- HIPAA-aligned monitoring and logging
- Scalable architecture for hospital-grade load
The result was a high-performing, resilient cloud app that improved patient workflows while maintaining compliance and reliability at scale.
Stat sourced from the CNCF 2023–2024 Annual Survey
FAQs
1. What exactly makes an application “cloud-native”?
A cloud-native app is built specifically for the cloud, not just moved to it. It uses modern tools like microservices, containers, and automated deployments so it can scale easily, recover faster after failures, and run smoothly across different cloud platforms. In simple terms, it’s an app designed to grow and survive in the cloud without needing constant manual work.
2. How do I choose between AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud for my application?
Think about your existing setup and long-term plans.
- AWS works well if you want the widest range of cloud tools and global reach.
- Azure fits perfectly for teams already using Microsoft tech like .NET or Active Directory.
- Google Cloud is great if your product relies heavily on analytics, AI, or data processing.
Most companies choose based on where their team feels comfortable and what gives the best mix of performance and cost.
3. How do cloud-native apps improve scalability?
Cloud-native apps are built in smaller parts that run independently. When traffic increases, only the parts that need more power scale up automatically. This means your app stays fast even during heavy usage, and you don’t need to overpay for servers running 24/7.
4. Are cloud-native apps more secure than traditional apps?
Yes, when they’re built and managed properly. Cloud providers offer strong, built-in security like identity controls, data encryption, and compliance certifications. Combined with secure coding, regular updates, and automated pipelines, cloud-native apps often end up safer than older monolithic systems.
5. What role does CI/CD play in cloud-native development?
CI/CD acts like an automated assembly line for your app. Every time your team updates code, CI/CD tests it, packages it, and prepares it for release. This reduces downtime, prevents human mistakes, and makes it possible to deliver updates faster without affecting users.